ECG Review for NCLEX RN
Telemetry strips often come up on the NCLEX. You need to be able to look at them, identify what they are and know which interventions are best. Here is a beat of a heart. You must remember this as well as certain abnormalities will tell you imminent life threatening situations.
![The PQRST complex. Image reproduced from [3] .](http://3.97.147.108/wp-content/uploads/2021/05/image.jpeg)
Key facts:
- Elevated T wave is an indicated of elevated potassium (K)
- Elevated ST segment = myocardial ischemia, risk factor for myocardial infarction
- Decreased ST segment = myocardial ischemia, risk factor for myocardial infarction
- P wave is atrial depolarization, without a p-wave identifiable it is not a “sinus” rhythm. No p wave = not sinus
- QRS = ventricular contraction
- Narrow QRS = promote vasovagal maneuvers, consider adenosine, betablocker, calcium channel blockers, cardioversion
- Wide QRS = consider antiarrhythmic (amiodarone, procanimide)
Basic rhythms:
- Normal sinus rhythm is 60 – 100 beats per minute
- Sinus bradycardia less than 60 beats per minute.
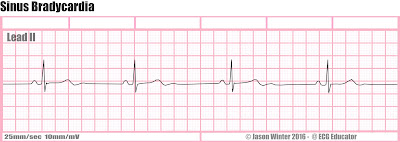
- Treatment of choice is atropine
- Sinus tachycardia is above 100 beats per minute.

- Treatment: based on cause.
- Fever = antipyretic
- Stimulant = STOP taking it.
- Anxiety = breathing techniques
- Pain = give pain medications.
- Sinus arrythmia:
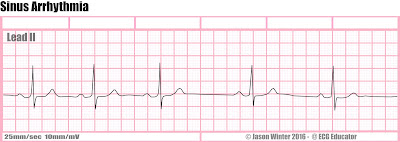
- Rhythm looks sinus but something is off. Ex) The pattern is irregular.
Atrial Rhythms:
- Atrial flutter

- Distinction: Saw tooth shape
- Risks: stroke, pulmonary embolism
- Treatment: cardioversion, antidysrhythmic, slow ventricular rate, heparin
- Atrial fibrillation

- Distinction: no p-wave
- Risks: stroke, pulmonary embolism
- Treatment: rate control, antithrombic therapy, correction of rhythm
- Rate control medications: Calcium Channel Blockers, Digoxin
- Supraventricular tachycardia
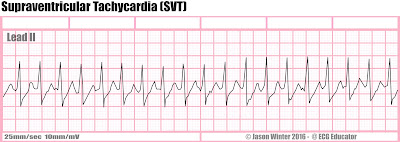
- Distinction: wide QRS, Constant QRS
- Risks: Heart failure
- Treatment: Adenosine
- If asymptomatic promote Vasovagal maneuver
- If unstable cardioversion and IV access
- Premature atrial contractions

- Not an actual rhythm.
- Distinction: p wave is above isoelectric line
- Think of it is a sporatic beat randomly that has no real cause.
- Happens to health patients.
Ventricular Rhythms:
- Premature ventricular contractions:

- Distinction: all of a sudden a random QRS
- Ventricular – these indicate a pattern of frequently it occurs
- Bigeminy = occurs every other beat consistently
- Trigeminy = occurs every third beat consistently
- Couplets = two together
- No real treatment, assess patient.
- Risk of converting into ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation
- Idioventricular rhythms:

- Ventricular escape rhythm
- Rate is >20 and <40
- Sinoatrial node failure or atrioventricular node failure you get this rhythm.
- Treatment:
- Atropine, pacing, dopamine, CPR
- Ventricular tachyardia:

- Distinction: Wide QRS
- Causes: Myocardial infarction, electrolyte imbalance
- Treatment: depends on situation
- Pulse present: unstable or chronic?
- If unstable: cardiovert, amiodarone, lidocaine
- No pulse present: code blue, CPR, defibrillate
- Chronic:
- Consider ICD placement
- Antiarrhythmics
- Pulse present: unstable or chronic?
- Ventricular fibrillation:

- Distinction: QRS constant but different sizes
- Treatment: defibrillate
- Vfib=defib
- Torsades de pointes:

- Distinction: QRS in a pattern
- Heart rate: 150 – 250 beats per minute
- Causes:
- Prolong QT interval:
- Electrolyte disturbances: Decrease in Magnesium and Potassium
- Treatment:
- Code blue – CPR
- Magnesium Sulphate bolus
- Unstable patient then synchronized cardioversion
- Pulseless electrical activity:

- Distinction: Normal Sinus Rhythm but no pulse.
- Hypovolemia is #1 cause
- Treatment: CPR
- Asystole:
- Distinction: Flat line
- Treatment: CPR
Key priority principles with EVERY rhythm:
- Always assess the patient.
- Ensure patent intravenous access.
- Check the pulse.


bookmarked!!, I love your site!
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here.
The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish.
nonetheless, you command get got an impatience over that you wish be
delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly again as exactly the
same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this increase.
Cool blog! Is your theme custom made or did you
download it from somewhere? A design like yours with a few simple tweeks would really make my blog stand out.
Please let me know where you got your design. Appreciate it
Hi, this weekend is fastidious for me, since this point in time i am reading this
impressive informative post here at my home.